Controversy has surrounded vitamin D research ever since it became public knowledge in 2014 that the Institute of Medicine had made a statistical error when developing the recommendation for vitamin D (underestimating it by 10-fold).
Almost 10 years later, they have still not fixed the error, or even publicly addressed it.
When an error goes unfixed in the face of correct knowledge, it insinuates perverse incentives. Normal people admit and fix knowable errors after they become known, but those with perverse incentives will try to avoid fixing errors (because the errors are intended by them, rather than being accidental).
A recent ‘error’ that is continuing to be made regarding vitamin D is the publishing of various meta-analyses which do not perform subgroup analysis so as to isolate studies giving moderate levels of vitamin D daily (rather than as a large bolus). Importantly, by lumping the bolus dosing studies up with the rest, you can make it appear as if vitamin D doesn’t have significant mortality benefit for COVID.
But when you do so, whether you have a Ph.D. or not, then you are engaged in a form of lying.
Back in 2019, it had been shown that bolus dosing of vitamin D — i.e., where tens or even hundreds of thousands of international units are given all at once — does not help with acute respiratory infections, while daily dosing does.
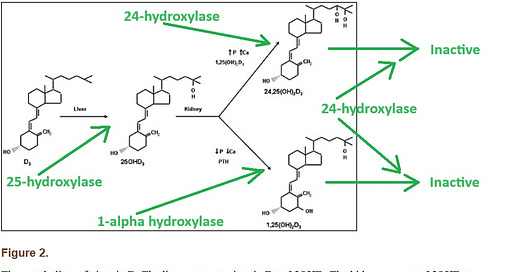
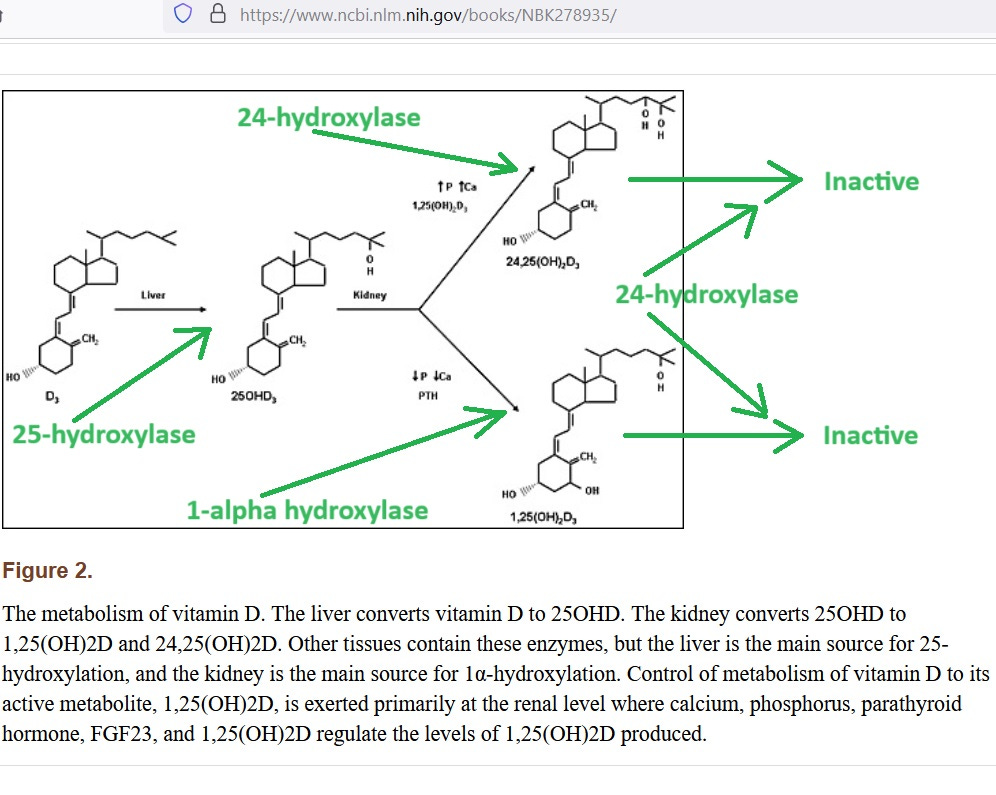
Two years later, a review of the matter made it clear to the scientific community that bolus dosing of vitamin D is a substandard practice. Here is a graph of vitamin D metabolism that is needed to explain (green marks added):
The fully-activated form of vitamin D is at bottom right. The 1-alpha hydroxylase enzyme catalyzes the activation, and the 24-hydroxylase enzyme (the “enemy” in this graph) breaks down activated vitamin D — making it inactive.
Guess what dosing regimen locks 24-hydroxylase in the “on” position for 6 weeks beyond when you stopped dosing?
That’s right, bolus dosing locks-in the “enemy” of vitamin D for 6 weeks. The result is that you get benefits for 7 to 30 days, and then harms, as induced 24-hydroxylase continues to rob your body of active vitamin D.
Here are results of a meta-analysis of mortality benefits for vitamin D with a re-analysis showing that — when you do subgroup analysis on daily dosing only — the mortality benefit from vitamin D is phenomenal against COVID:
Rows 26 to 47 came from the published meta-analysis, while work below that is mine. A crude (summary) relative risk, or RR, for the daily dosing trials (cell G63) shows 43% reduced death (RR = 0.57). The median of the published RR values is still 0.6 — indicating 40% reduction in risk of death.
Even the third quartile RR of the daily dosing studies indicated benefit (RR = 0.9).
To the credit of the researchers who performed this meta-analysis, they did do a sensitivity analysis called “leave one out” — where they repeat the analysis with one study left out, running through all studies, to find out if leaving out any single trial changed the results.
They found out that, if they left out a big trial that used bolus dosing (Cannata-Andia, 2022), then vitamin D became life-saving — as found in the Data Supplement to the study.
Reference
Papadimitriou DT. The Big Vitamin D Mistake. J Prev Med Public Health. 2017 Jul;50(4):278-281. doi: 10.3961/jpmph.16.111. Epub 2017 May 10. PMID: 28768407; PMCID: PMC5541280. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28768407/
“Another study confirmed that 6201 IU/d was needed to achieve 75 nmol/L and 9122 IU/d was needed to reach 100 nmol/L. The largest meta-analysis ever conducted of studies published between 1966 and 2013 showed that 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels <75 nmol/L may be too low for safety and associated with higher all-cause mortality, demolishing the previously presumed U-shape curve of mortality associated with vitamin D levels.”
Martineau AR, Jolliffe DA, Greenberg L, Aloia JF, Bergman P, Dubnov-Raz G, Esposito S, Ganmaa D, Ginde AA, Goodall EC, Grant CC, Janssens W, Jensen ME, Kerley CP, Laaksi I, Manaseki-Holland S, Mauger D, Murdoch DR, Neale R, Rees JR, Simpson S, Stelmach I, Trilok Kumar G, Urashima M, Camargo CA, Griffiths CJ, Hooper RL. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: individual participant data meta-analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2019 Jan;23(2):1-44. doi: 10.3310/hta23020. PMID: 30675873; PMCID: PMC6369419. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6369419/
“Subgroup analysis revealed that protective effects were seen in individuals receiving daily or weekly vitamin D without additional bolus doses (aOR 0.81, 95% CI 0.72 to 0.91), but not in those receiving one or more bolus doses (aOR 0.97, 95% CI 0.86 to 1.10; p = 0.05).”
Mazess RB, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Dawson-Hughes B. Vitamin D: Bolus Is Bogus-A Narrative Review. JBMR Plus. 2021 Oct 30;5(12):e10567. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10567. PMID: 34950828; PMCID: PMC8674779. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8674779/
“Notably, the elevated 24,25(OH)2D persisted for 6 weeks after dosing ended, reflecting the longer‐term induction of 24‐hydroxylase blocking the formation of 1,25(OH)2D.”
Meng J, Li X, Liu W, Xiao Y, Tang H, Wu Y, Xiong Y, Gao S. The role of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr. 2023 Nov;42(11):2198-2206. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.09.008. Epub 2023 Sep 20. PMID: 37802017. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37802017/
“For the mortality, after excluding the study by Cannata-Andia et al., vitamin D supplementation significantly reduced the mortality of the patients (eFig. 5 in supplement).”




Imagine if they would have done 5k vitamin D3 with magnesium and a mix of K2 mk5 and mk7. Wait that’s a four-vitamin protocol way too complicated... and way too effective. That would be like using zinc and quercertin and vitamin C to treat covid. But they will do multiple drug combinations for heart disease - statin, beta blocker, diuretic, hyper blood pressure medication and heart drug of the day as a multi-drug protocol.