The WHO’s minimum acceptable standard for effectiveness against COVID is a central estimate of 50% and a confidence boundary at least as high as 30%. Vitamin D met the WHO standard, but the COVID booster shots after June 2022 (after Omicron BA.2) all failed to meet the WHO standard for being “effective.”
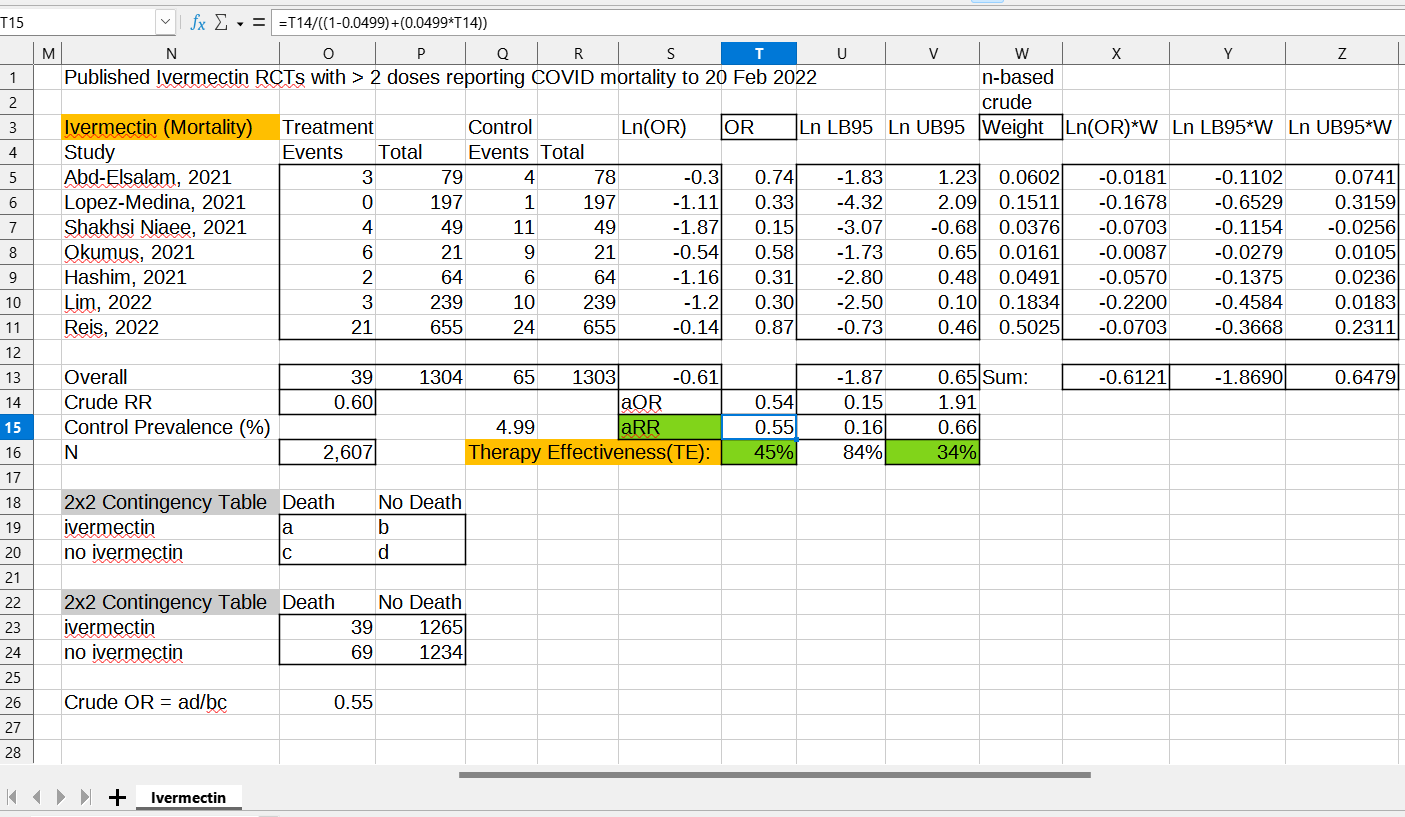
Here is a re-analysis of an original meta-analysis (PMC9191543), but with the three single- and double-dose ivermectin trials removed:
[click to enlarge]
The weights in column W are based on trial size. The central estimate of effectiveness in preventing death in COVID patients (in cell T16) was 45%, and the confidence boundary (cell V16) was still 34% effectiveness against death.
Published clinical trial data on multi-dose ivermectin reveals that it should be recommended by WHO, because it is close enough to meeting their standard of effectiveness.
Reference
[original meta-analysis of published ivermectin clinical trials] — Shafiee A, Teymouri Athar MM, Kohandel Gargari O, Jafarabady K, Siahvoshi S, Mozhgani SH. Ivermectin under scrutiny: a systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and possible sources of controversies in COVID-19 patients. Virol J. 2022 Jun 13;19(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8. PMID: 35698151; PMCID: PMC9191543. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9191543/