WHO Standards applied to Remdesivir
Post #540
The minimum acceptable standards for COVID intervention (at least for “vaccines”) require that the central estimate of effectiveness is 50% with a 95% lower bound estimate of 30%.
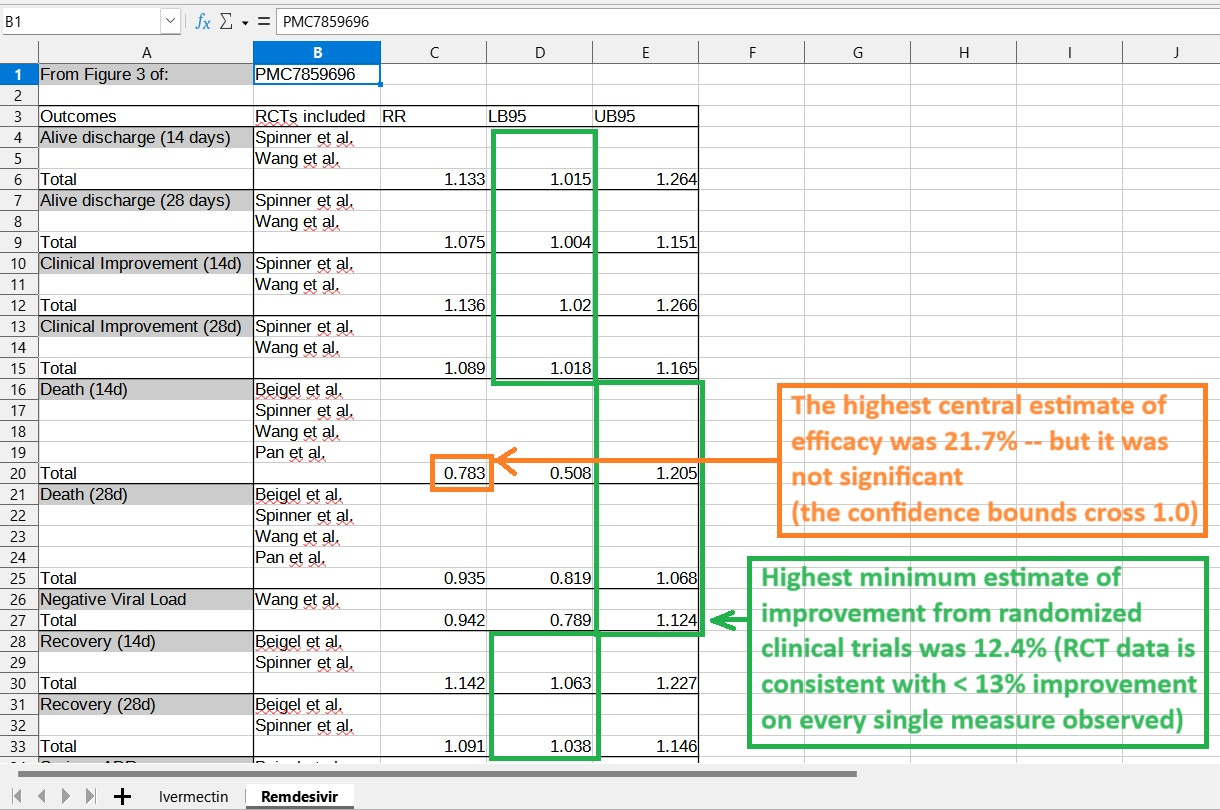
Here is how remdesivir stacks up, using results from a meta-analysis published online in Feb 2021:
Remdesivir failed to meet the “50% effective” standard using the central estimates. In cell C20, the relative risk of .783 means that the benefit or effectiveness is 1-.783 = .217, or 21.7% effectiveness.
Even still, that central estimate was not signficant because the bounds of precision on it crossed over the threshold at 1.0 — where treatment is no more effective than placebo.
Looking at just the lower bounds, and trying to find one that is consistent with at least 30%, also reveals that remdesivir fails on all accounts (on all outcomes measured). In fact, the highest minimum effect was 12.4%, meaning that all randomized clinical trial data on remdesivir was consistent with less than 13% improvement.
Peer-reviewed evidence suggests that substances such as vitamin D and ivermectin are much more effective against COVID than remdesivir, and they are much safer as well. It is a shame that officials didn’t recommend them, even though they are more safe, and more effective, than remdesivir (which did get recommended).
Reference
[meta-analysis on remdesivir] — Rezagholizadeh A, Khiali S, Sarbakhsh P, Entezari-Maleki T. Remdesivir for treatment of COVID-19; an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 15;897:173926. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173926. Epub 2021 Feb 4. PMID: 33549577; PMCID: PMC7859696. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7859696/


Excellent. Thanks again. I hope someone uses this in court when Fauci is on trial for treason.